Governance, risk, and compliance, often called GRC, is a blanket term that describes the strategies and technologies used to manage an organization’s compliance with regulatory mandates and corporate governance standards.
The concept of GRC can be traced back to 2003, but the topic was first extensively discussed in a peer-reviewed paper by Scott L. Mitchell, published in the International Journal of Disclosure and Governance in 2007. This guide discusses what GRC is and what it can mean for you and your business.
What is GRC?
GRC is an organization’s overall strategy in tackling its three interrelated aspects. To better understand GRC, it’s best to look into each individual component.
Governance
The framework of rules, processes, and practices by which an organization is directed and managed. In essence, this comprises how an organization attempts to meet its goals and business objectives.
Risk or risk management
The potential for loss or damage to an organization’s reputation, finances, employees, customers, or other stakeholders. In particular, the main focus of risk in GRC is risk management, i.e,., identifying and subsequently minimizing risks encountered by the organization.
Compliance
The state of conforming to laws, regulations, and standards required by relevant bodies or government agencies. This can vary depending on the industry or sector and ensures that organizations meet a minimum standard of operations.
What drives GRC?
There is no question that regulation is the current biggest driver of GRC. Industries such as healthcare, financial services, and technology companies have borne the brunt of regulatory measures. Amazon’s massive GDPR fine of $877 million has been fresh on our minds since it was announced in its 2021 Q2 earnings report filed with the SEC.
More recently, Meta Platforms Ireland was fined €1.2 billion in 2023 by the Irish Data Protection Authority for violating data privacy laws with its popular social media platform, Facebook. In particular, Meta failed to adhere to the EU’s GDPR for its unauthorized transfer of Facebook user data from the EU to the US servers.
But another important driver of GRC is corporate governance. Investors are increasingly interested in how companies are managed and what kind of risks they are exposed to. Moreover, employees, customers, and other stakeholders expect organizations to be transparent about their operations and have robust mechanisms to prevent misconduct.
Operational risks associated with the day-to-day operations of an organization also drive GRC. These include risks related to information security, supply chain management, and employee safety.
Why is GRC important?
GRC is important because it helps organizations protect their reputations, finances, customers, and employees while ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Moreover, GRC can also help organizations improve their operational efficiency and reduce costs.
By implementing a GRC program, organizations can avoid costly fines, penalties, and litigation expenses associated with non-compliance. In addition, a well-run GRC program can help organizations spot potential problems before they occur, saving them time and money in the long run.
SEE: Securing Linux Policy (TechRepublic Premium)
What are some GRC tools?
In recent years, the corporate emphasis on GRC has given rise to a new breed of GRC software that is helping organizations of all sizes automate and streamline their GRC processes. Here are just a few examples:
Compliance management systems
These systems help organizations keep track of their compliance obligations by providing them with real-time visibility into their compliance posture. In addition, they typically include workflow capabilities that make it easy for organizations to manage their compliance processes from start to finish.
Risk management systems
These help organizations identify, assess, and manage operational risks. They typically include features such as risk dashboards and heat maps that give organizations a quick way to see where their biggest risks are located.
Policy management systems
These systems help organizations develop, implement, and enforce corporate policies and procedures. They typically include features such as policy templates and workflows that make it easy for organizations to create and distribute policies throughout their company.
There are also unified platforms that offer a complete suite of GRC capabilities in one place. These platforms are often used by enterprises that need to manage complex GRC programs.
If you want a more extensive look into GRC software tools and providers, I encourage you to check out our Best GRC Tools guide.
In that feature, we dive into which GRC tools are best for scalability, visibility, risk management, and more. We also discuss which types of businesses can gain the most benefit from using GRC tools.
How to implement GRC in your organization
When it comes to implementing a GRC program, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The best approach will vary depending on the size, complexity, and needs of your organization.
A strong approach to GRC implementation is offered through the GRC Capability Model (Red Book) developed by OCEG. The model has four components: LEARN, ALIGN, PERFORM, and REVIEW.
Let’s discuss each key component below.
LEARN how GRC relates to your specific business needs
The first step is to clearly understand the laws, regulations, standards, culture, stakeholders, and the entire context that applies to your organization. You should also assess your organization’s risk tolerance and establish what kind of risks you are willing to take. This will inform your objectives, strategies, and actions.
ALIGN your strategy with greater business objectives
The next step is to align your GRC strategy with your organizational objectives and actions. This will help your GRC program to align with the overall goals of your organization
PERFORM actions and policies toward desirable results
The third step is to take actions that reinforce the desirable and neutralize the undesirable. You should also take action to help you detect deviations from GRC policies and procedures as soon as possible.
REVIEW and evaluate GRC on an ongoing basis
The fourth and final stage of this GRC model is to evaluate the strategy’s design, operational effectiveness, and continuing relevance of goals to improve your organization.
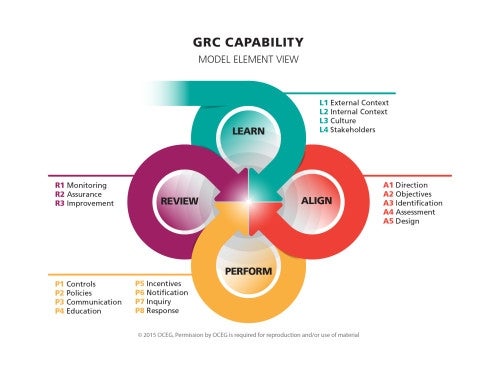
The GRC Capability Model provides an excellent framework for thinking about and implementing GRC in your organization. When implemented correctly, a GRC program can help organizations take a proactive stance on GRC — which is crucial to an organization’s success in today’s complex business environment.
This article was originally published in September 2022. It was updated by Luis Millares in January 2025.

