ITMF (International Textile Manufacturer Federation) has published its International Textile Industry Statistics (ITIS) on productive capacity and raw materials consumption in the short-staple organized (spinning mill-) sector in virtually all textile-producing countries in the world.
ITMF has published its International Textile Industry Statistics.
In 2022, global textile machinery like spindles and rotors surged, notably in Asia.
Shuttle-less looms surpassed shuttle ones, reaching 1.85 million versus 952 thousand.
Raw material use dipped to 44.26 million tons, with -2.5% in cotton, -0.7% in synthetics, and a 2.5% rise in cellulosic fibres.
The global number of installed short-staple spindles has grown from 225 million units in 2021 to 227 million units in 2022 (see Fig. 1). The number of installed open-end rotors increased from 8.3 million in 2021 to 9.5 million in 2022 (see Fig. 2). This constitutes the strongest growth ever recorded in this market with investment disproportionally targeting Asia. The number of installed air-jet spindles continued to increase in all regions in 2022.
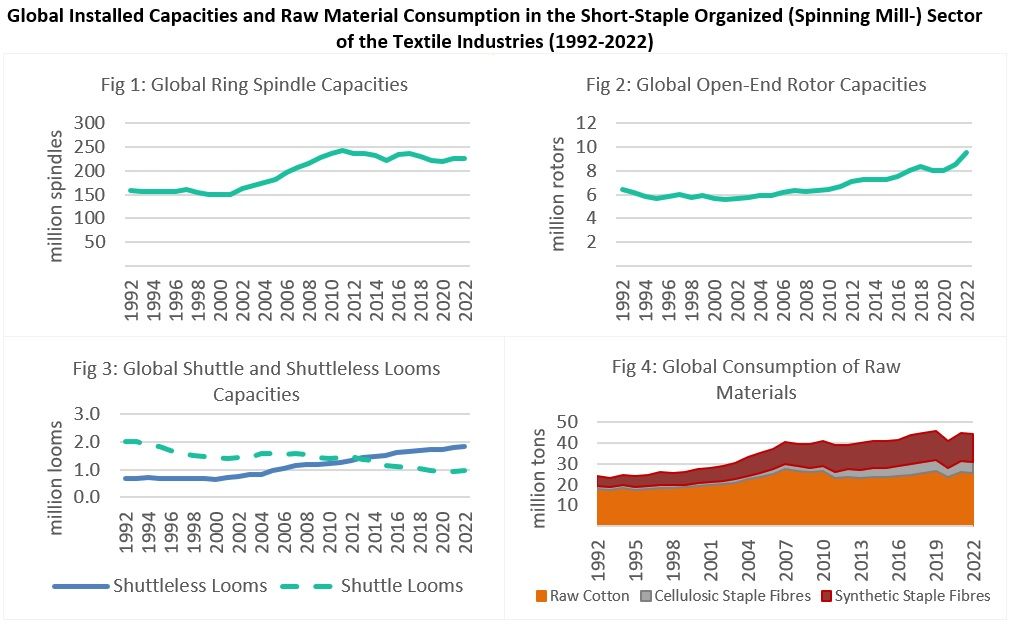
The substitution between shuttle and shuttle-less looms continued in 2022. The number of installed shuttle-less looms increased from 1.72 million in 2021 to 1.85 in 2022 (see Fig. 3) while installed shuttle looms reached 952 thousand. Total raw material consumption in the short-staple organized sector slightly decreased from 45,6 million tons in 2021 to 44,26 million tons in 2022 (see Fig. 4). Consumption of raw cotton and synthetic short-staple fibers decreased by -2.5% and -0.7%, respectively. Consumption of cellulosic short-staple fibers increased by 2.5%.
Note: The content of this press release has not been edited by Fibre2Fashion staff.
Fibre2Fashion News Desk (HU)

