Sleep is essential for maintaining physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. Despite its importance, many people fail to get the recommended amount of rest each night. A FITTR study of 1,340 wearable device users has provided insights into sleep patterns, stress levels, and their connection to overall health. The findings highlight widespread sleep deprivation, gender differences in sleep duration, and the impact of sleep on recovery and stress.
Here we explore the key takeaways from the study and how sleep quality affects health.
Key Findings on Sleep and Health
1. Sleep Deprivation is Widespread
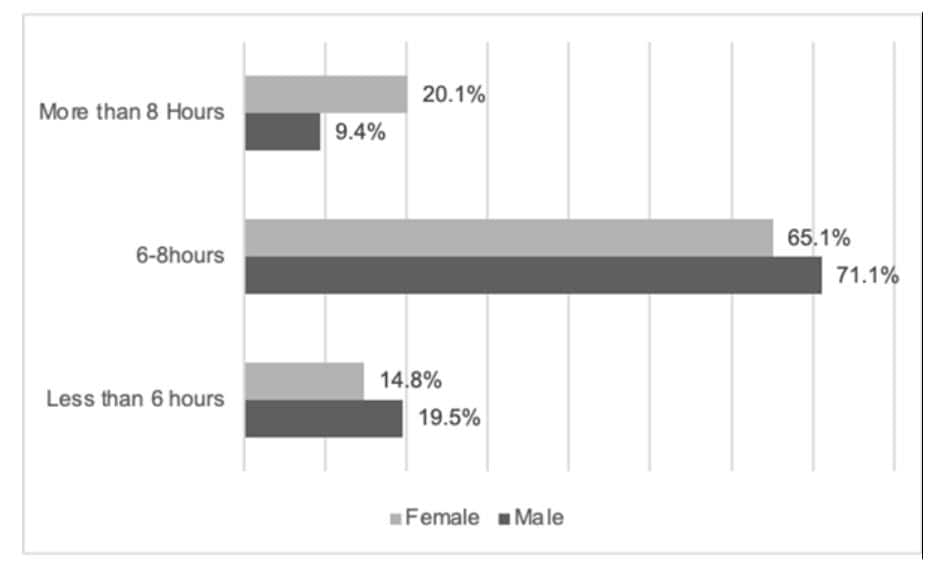
→ Over 87% of participants slept lesser than the recommended 8 hours per night.
→ Nearly 20% of users slept fewer than 6 hours, putting them at risk for long-term health issues.
2. Women Sleep More Than Men
→ On average, women slept 7.01 hours per night, while men averaged 6.68 hours.
→ This aligns with previous studies that show women tend to have longer sleep durations than men.
3. Sleep Quality Affects Recovery
→ Individuals who slept longer, especially in deep sleep, showed better recovery levels.
→ Deep sleep plays a crucial role in muscle repair, immune function, and cognitive performance.
4. Sleep and Stress Are Closely Linked
→ Participants with shorter sleep durations reported higher stress levels.
→ The study confirmed that inadequate sleep increases stress, creating a cycle of poor rest and mental strain.
5. Poor Sleep Leads to Serious Health Risks
Chronic sleep deprivation was associated with increased risks of:
→ Heart disease
→ Cognitive decline
→ Impaired physical performance
→ Higher likelihood of obesity and diabetes
6. Sleep Duration Declines with Age
→ Older adults (50+) had shorter sleep durations, averaging 6.2 hours per night.
→ This trend is linked to a higher risk of chronic illnesses.
How Sleep Affects the Body
1. Recovery and Physical Performance
During deep sleep, the body repairs tissues, balances hormones, and strengthens the immune system. Poor sleep can lead to:
→ Slower muscle recovery
→ Increased fatigue
→ Reduced energy and endurance
2. Mental Health and Stress Management
Lack of sleep contributes to anxiety, depression, and increased stress. The study found that:
→ Sleep-deprived individuals were significantly more likely to develop anxiety and depression.
→ Chronic stress further reduces sleep quality, creating a negative cycle.
3. Long-Term Health Impacts
→ Sleep deprivation increases inflammation, which is linked to heart disease and metabolic disorders.
→ Poor sleep weakens the immune system, making individuals more vulnerable to illnesses.
How to Improve Sleep for Better Health
For better sleep and overall well-being, consider these strategies:
→ Maintain a consistent sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time daily helps regulate the body’s internal clock.
→ Limit screen time before bed: Blue light from screens interferes with melatonin production.
→ Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Activities such as reading or meditation can improve sleep quality.
→ Ensure a comfortable sleep environment: A cool, dark, and quiet room promotes restful sleep.
→ Avoid caffeine and heavy meals late at night: These can disrupt sleep patterns.
Sleep is a crucial component of overall health, influencing everything from physical recovery to stress levels. The study highlights the widespread issue of sleep deprivation, gender-specific sleep trends, and the importance of quality rest for well-being. Addressing sleep issues through better habits and lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve health outcomes. Prioritizing sleep is essential for maintaining a balanced and healthy life.

